
Are you ready to supercharge your e-commerce business and watch your sales soar? If so, you’ve come to the right place. In the fast-paced world of online retail, one thing is clear: to thrive, you need to be where your customers are, and that place is often Google. With its vast user base and powerful advertising platform, Google Ads is a game-changer for e-commerce businesses, but success is not guaranteed. To make the most of your advertising budget and drive conversions, you must master the art of Google Ads Shopping Campaign Structure.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll take you on a journey through the intricate world of Google Ads, focusing specifically on the structure of Shopping Campaigns. By the time you finish reading, you’ll be armed with the knowledge and strategies to optimize your campaign structure and unlock the full potential of your e-commerce store.
Whether you’re a seasoned digital marketer looking to refine your skills or a newcomer trying to navigate the world of online advertising, this guide will provide you with the insights and techniques you need to achieve e-commerce success. So, let’s dive in and discover how to structure your Google Ads Shopping Campaign for maximum impact and profitability.
Understanding Google Ads Shopping Campaign Structure
Google Ads Shopping Campaigns represent a cornerstone of e-commerce advertising. These campaigns allow you to showcase your products directly in Google’s search results, complete with eye-catching images, prices, and essential store information. This visually engaging approach has the potential to significantly increase click-through rates and conversions for your products.
To leverage this powerful tool, it’s crucial to understand how Shopping Campaigns work and how to structure them effectively.
Setting the Foundation: Campaign and Ad Group Structure
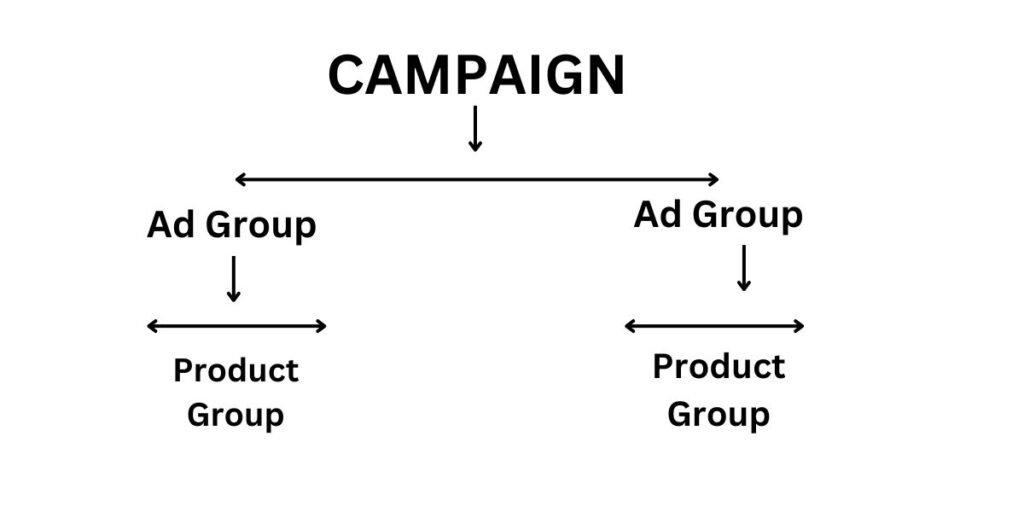
Creating a new Shopping Campaign is your first step, but it’s the structure within your campaign that sets the stage for success. Organizing your ad groups effectively is vital. Ideally, each ad group should be dedicated to a specific product category or type. This level of granularity enables you to tailor your targeting and bidding strategies with precision.
Let’s dig deeper into this foundation-building process:
Creating a New Shopping Campaign: When creating your campaign, select the “Shopping” campaign type in Google Ads. You’ll be prompted to choose your campaign settings, including your campaign’s name, daily budget, and bidding strategy.
Organizing Ad Groups: Within your campaign, you’ll create ad groups. These are like thematic buckets for your products. For instance, if you’re selling clothing, you might create separate ad groups for “Men’s Apparel,” “Women’s Apparel,” and “Accessories.” Within each ad group, you’ll add the relevant products.
Segmenting Products: Effective segmentation is critical for precise targeting. Consider segmenting your products based on attributes like brand, price range, or product type. This segmentation allows you to allocate budgets and set bids according to the performance of each group.
By paying close attention to your campaign and ad group structure, you’ll lay the groundwork for more efficient and profitable campaigns.
Product Feed Optimization
Your product feed is the lifeblood of Google Shopping Campaigns. Think of it as the bridge between your e-commerce store and Google Ads. Google uses the information in your product feed to determine when and where to display your products in search results.
Here are some key aspects to consider when optimizing your product feed:
Quality Images: High-quality images are paramount. Ensure that your product images are clear, well-lit, and showcase your products from multiple angles if possible. Shoppers are more likely to click on listings with visually appealing images.
Detailed Descriptions: Your product descriptions should be informative and engaging. Highlight the key features and benefits of each product. Include essential details such as size, color, material, and any unique selling points.
Accurate Pricing: Keep your product prices up-to-date. Nothing frustrates potential customers more than clicking on a product only to find that the price has changed. Google may disapprove ads with inaccurate pricing.
Structured Data: Use structured data markup to provide Google with additional information about your products. This can enhance the visibility and richness of your product listings in search results.
Feed Optimization Tools: Consider using feed optimization tools or services to streamline the process. These tools can help you ensure that your product feed meets Google’s requirements and performs at its best.
Remember, your product feed is the foundation upon which your Shopping Campaigns are built. Take the time to optimize it thoroughly to maximize your campaign’s effectiveness.
Keyword and Negative Keyword Strategies
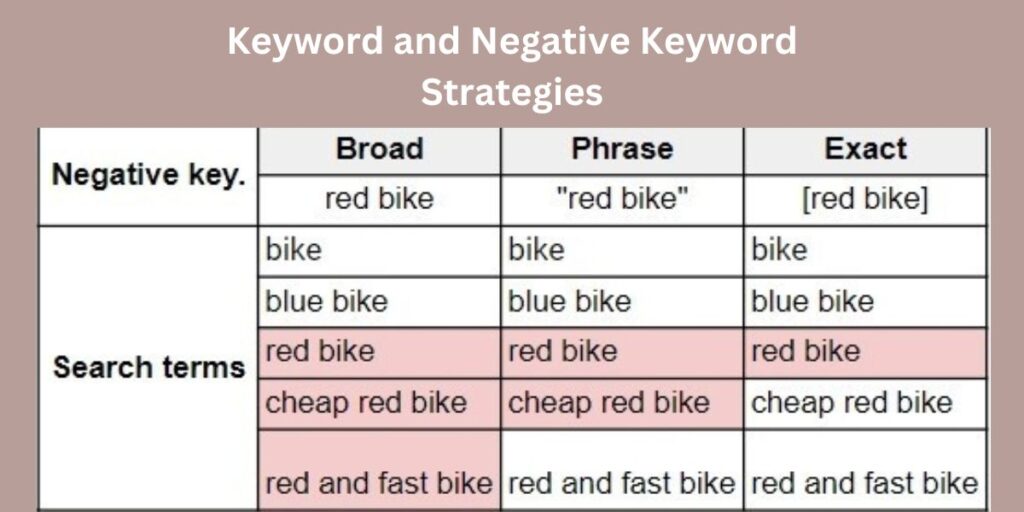
Keywords play a vital role in Google Ads. They are the words and phrases that trigger your ads to appear when customers search on Google. For Shopping Campaigns, selecting the right keywords for your products is essential. This often involves keyword research to identify popular search terms related to your items.
Choosing Relevant Keywords: Start by brainstorming a list of keywords that are relevant to your products. Think about what terms your potential customers might use when searching for products like yours.
Keyword Match Types: Google Ads offers different keyword match types: broad match, phrase match, exact match, and broad match modifier. Each type has its advantages and considerations.
- Broad Match: Your ads may show for a wide range of search queries related to your keywords.
- Phrase Match: Your ads will show for searches that include your keyword phrase in the specified order.
- Exact Match: Your ads will only show for searches that exactly match your keyword.
- Broad Match Modifier: Allows for more control over broad match by specifying certain terms that must be present in the user’s query.
Negative Keywords: Negative keywords are equally important. These are keywords for which you do not want your ads to appear. For example, if you’re selling high-end luxury watches, you might add “cheap” or “affordable” as negative keywords to avoid clicks from users looking for budget options. Negative keywords help you refine your targeting and avoid irrelevant clicks that could drain your budget.
Effective keyword selection and management are ongoing processes. Regularly review your keyword performance and adjust your list as needed to improve campaign efficiency.
Bidding and Budget Management

Effective bidding is a cornerstone of successful Google Ads campaigns. While Google offers various bidding strategies, selecting the right one depends on your goals and budget. Here are some strategies to consider:
Manual Bidding: With manual bidding, you set the maximum amount you’re willing to pay for a click on your ad. This gives you full control over your bids but requires active monitoring and adjustment.
Enhanced CPC (eCPC): eCPC is a semi-automated bidding strategy that adjusts your manual bids based on the likelihood of a conversion. Google’s algorithms analyze historical data to make these adjustments.
Target ROAS (Return on Ad Spend): If you have a specific target for your return on ad spend, this strategy allows you to set a target ROAS percentage. Google will adjust your bids to help you achieve this goal.
Maximize Clicks: This strategy aims to get as many clicks as possible within your budget. It’s a good option if you’re focused on driving traffic to your site but should be used with caution, as it may not prioritize profitable clicks.
Budget Allocation: Determining how to allocate your budget among different campaigns and ad groups is a crucial consideration. High-performing campaigns may warrant higher budgets, while others may need adjustment or pausing if they’re not delivering results.
Bid Adjustments: Google Ads allows you to make bid adjustments based on various factors such as location, device type, and time of day. Use these adjustments strategically to fine-tune your targeting and budget allocation.
The key to successful bidding and budget management is continuous monitoring and adjustment. Be prepared to review your campaigns regularly, analyze their performance, and make changes to improve your ROI.
Ad Copy and Extensions
Crafting compelling ad copy is essential in attracting clicks and driving conversions. Your product titles and descriptions should not only be informative but also persuasive. Here are some tips for creating effective ad copy:
Clear and Concise Titles: Your product titles should be clear and concise. Use the most important keywords at the beginning of the title to catch the user’s attention. For example, “Designer Leather Handbag – 40% Off.”
Compelling Descriptions: In the description, highlight the key features and benefits of your product. Be concise but provide enough information to entice users to click. Mention any unique selling points, such as free shipping, discounts, or limited-time offers.
Call to Action (CTA): Include a strong call to action in your ad copy. Phrases like “Shop Now,” “Buy Today,” or “Limited Stock” can encourage users to take action.
Ad Extensions: Ad extensions are additional pieces of information that you can add to your ads to provide more value to potential customers. Google offers several types of ad extensions, including:
- Sitelink Extensions: These allow you to include links to specific pages on your website, such as product categories or special promotions.
- Callout Extensions: Callout extensions enable you to highlight key selling points or features, such as “Free Shipping” or “24/7 Customer Support.”
- Structured Snippet Extensions: These extensions let you showcase specific aspects of your products or services, such as product categories or brands.
Use ad extensions strategically to enhance your ad’s visibility and appeal. Remember that the more information you provide in your ads, the more likely users are to click and convert.
Monitoring and Analytics
The success of your Google Ads Shopping Campaigns doesn’t end with setup. Continuous monitoring and data analysis are essential to fine-tune your campaigns and achieve optimal results. Let’s explore some key aspects of monitoring and analytics:
Key Metrics: Start by identifying the key performance metrics that matter most to your business. These may include:
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): The percentage of users who click on your ads after seeing them.
- Conversion Rate: The percentage of clicks that result in a desired action, such as a purchase.
- Return on Ad Spend (ROAS): The ratio of revenue generated to the cost of advertising.
- Impression Share: The percentage of impressions your ads receive compared to the total number of impressions they could potentially receive.
- Average Position: The average position at which your ads appear in search results.
Conversion Tracking: Implement conversion tracking to measure user actions on your website after clicking on your ads. This might include tracking purchases, sign-ups, or other valuable interactions.
Google Analytics Integration: Integrate Google Ads with Google Analytics to gain deeper insights into user behavior on your site. You can track user paths, behavior flows, and more.
Performance Trends: Pay attention to performance trends over time. Are there certain days of the week or times of day when your campaigns perform better? Are there seasonal fluctuations in demand for your products?
A/B Testing: Experiment with A/B testing to compare different ad variations and landing pages. This can help you identify what resonates most with your audience and optimize your campaigns accordingly.
Effective monitoring and analytics require both the right tools and the right mindset. Regularly review your campaign performance, make data-driven decisions, and be prepared to adjust your strategies based on your findings.
Troubleshooting and Common Challenges
Expect challenges along the way. The world of online advertising is dynamic, and issues can arise that impact your campaigns. Here are some common challenges and strategies for overcoming them:
Low Click-Through Rate (CTR): If your CTR is low, it may be due to unappealing ad copy, poor targeting, or low-quality product images. Consider revising your ad copy, refining your targeting, and optimizing your product feed.
High Cost Per Click (CPC): A high CPC can eat into your budget quickly. Review your keyword strategy, ad quality, and landing page experience to see if there are opportunities to reduce costs while maintaining performance.
Low Conversion Rate: If your conversion rate is below expectations, evaluate your landing page experience. Ensure that your landing pages are relevant to the ads and provide a smooth, user-friendly experience. Test different landing page elements to improve conversion rates.
Competitive Pressure: In competitive industries, it can be challenging to maintain visibility without overspending. Consider long-tail keywords, niche targeting, and unique selling propositions to stand out from competitors.
Ad Disapprovals: Google Ads has strict policies, and ads that violate these policies may be disapproved. Review Google’s advertising policies to ensure compliance, and make necessary adjustments to your ads or landing pages.
Remember that troubleshooting is an ongoing process. As you encounter challenges, don’t get discouraged; view them as opportunities for improvement. Small adjustments can often lead to significant improvements in campaign performance.
Advanced Tips and Strategies
For those looking to take their Google Ads Shopping Campaigns to the next level, consider exploring advanced tactics and strategies. Here are a few advanced tips to consider:
Dynamic Remarketing: Dynamic remarketing allows you to show tailored ads to users who have previously visited your website or viewed specific products. This highly personalized approach can significantly boost conversion rates.
Audience Targeting: Explore audience targeting options to reach users who are more likely to convert. Use demographic, interest, and behavior-based targeting to fine-tune your audience segments.
Automation and Machine Learning: Google Ads offers automation features powered by machine learning. Experiment with automated bidding strategies and ad rotation to leverage Google’s algorithms for optimization.
Segmentation and Customization: Create highly segmented campaigns and ad groups to cater to different audience segments or product categories. Tailor your ad copy and bidding strategies to match each segment’s preferences and behaviors.
Competitor Analysis: Keep an eye on your competitors. Analyze their ad strategies, keywords, and landing pages to identify opportunities and threats. Tools like Google’s Auction Insights can provide valuable competitive insights.
Ad Testing: Continuously test different ad variations to identify what resonates best with your audience. Experiment with ad headlines, descriptions, images, and offers to optimize your click-through and conversion rates.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering the structure of your Google Ads Shopping Campaigns can be the key to e-commerce success. By following the strategies and tips outlined in this guide, you’ll not only establish a strong foundation but also have the tools to adapt and evolve your campaigns over time. Your e-commerce success story awaits!
Remember that success in Google Ads requires ongoing effort and adaptation. Stay vigilant, test different strategies, and always strive for improvement. As you implement these tactics, you’ll be well on your way to optimizing your campaigns, increasing your ROI, and growing your online business.
Additional Resources
For further learning and assistance, consider these resources:
If you have any questions or need personalized guidance, feel free to reach out to us.
How Can We Help?
Need help with Advanced Google Ads Management for your Business Growth? Contact us and let’s discuss about effective Google Ads strategy that will take your business to the next level!
